Come Configurare Un Ssd M2
What is an M.2 SSD?
An M.two SSD is a pocket-sized form factor solid-state drive (SSD) that is used in internally mounted storage expansion cards. M.ii SSDs conform to a figurer industry specification and are designed to enable loftier-performance storage in thin, power-constrained devices, such every bit ultrabook laptops and tablet computers. They are generally smaller than other comparable SSDs, such as the mini Serial Advanced Engineering Attachment (mSATA).
SSDs are a form of storage media that saves persistent information on solid-state flash memory. Unlike a hd (HDD), an SSD has no moving parts to break or spin upwardly or down. The Yard.two SSD interface specification was originally known as the Side by side-Generation Form Factor, but the name was changed to Grand.2 (pronounced M-dot-two). Chiliad.2 SSDs are useful for someone who is building or upgrading a personal figurer (PC) or laptop for use cases such every bit gaming, 3D animation, video editing or large file transfers.
M.two supports multiple protocols and applications such equally Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) and SATA. M.two-compatible products are not limited to solid-land drives either. The specification also supports protocols such equally Universal Series Buses (USBs) and Wi-Fi and can be used in graphics cards and bogus intelligence accelerator cards that utilize the G.2 specification.
The Thousand.2 form-cistron specification was defined by the SATA International Organization, as well as the PCI Special Interest Grouping -- a consortium of technology industry vendors.
How does an M.2 SSD work?
M.2 modules can integrate with device classes such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, near-field communication and wireless wide surface area networks. Simply M.2 form factors are most commonly associated with SSDs for information storage.
M.ii drives do not need a cable to connect to a motherboard. Instead, they are plugged directly into the motherboard with a defended M.two connector slot.
An Chiliad.two SSD can exist used with both SATA and PCIe protocols. SATA is a standard for connecting and transferring data from HDDs to reckoner systems. PCIe, which is a serial expansion bus standard, is used to connect a computer to one or more than peripheral devices.
G.2 SSDs also back up PCIe-based not-volatile memory express (NVMe) drives. NVMe can accelerate the transfer speed of data between client systems and SSDs over a PCIe coach. NVMe support was adult to reduce bottlenecks and better performance. It too enables increased parallel processing for read and write requests. Considering of its design, NVMe back up tin add together upwardly to five times more than bandwidth than SATA 1000.ii models and may enable a computer to provide better performance for tasks like file transfers.
M.2 SSDs tin can also be either single- or double-sided. Single-sided Chiliad.2 boards are used where space is limited, such as with ultra-thin laptops. Double-sided chips, however, take upwards more concrete space but take greater storage capacities.
The M.two device has notches in one end, which human activity as connectors, called module keys. M.2 modules are rectangular. An edge connector is located on i side with a mounting pigsty at the reverse edge. The border connector has 75 positions with up to 67 pins. Each pivot is rated up to 50 volts and 0.5 amps.
M.ii SSD form factor
Generally, M.2 SSDs are 22 millimeters wide and 60 mm or 80 mm long; although, card lengths can vary. The card size is identified by a iv- or five-digit number. The first two digits are the width and the remaining numbers are the length. For example, a 2260 carte is 22 mm wide and 60 mm long. Longer M.2 drives commonly hold more NAND chips for actress capacity. Other sizes include:
- 2280 -- 22 mm x 80 mm
- 2230 -- 22 mm x 30 mm
- 2242 -- 22 mm x 42 mm
- 2260 -- 22 mm x 60 mm
- 22110 -- 22 mm x 110 mm
The 22 mm width is the standard for desktops and laptops. An 80 mm or 110 mm length card can agree eight NAND chips for two terabytes (TB) of capacity.
M.ii module keys
Keys -- the notches in the edge connectors of M.two modules -- tin distinguish the type of G.2 product.
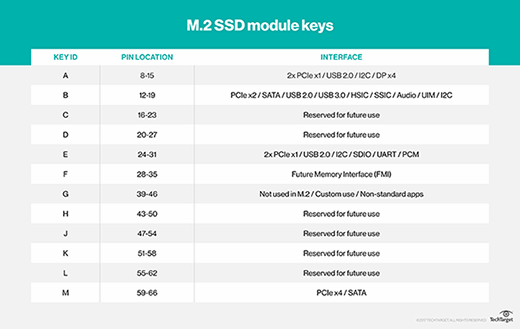
M.two SSD modules plug into excursion boards through connectors on either side. Unlike mSATA, 1000.ii SSD cards have 2 types of connectors, also known as sockets: B central sockets and M key sockets. A single carte can besides take both key types. The type of key determines the number of PCIe lanes the socket supports. A B fundamental holds one or two PCI express lanes, while an Thou key holds up to four PCIe lanes. The B key border connector is half dozen pins wide, and the Chiliad primal edge connector is five pins broad.
For Wi-Fi and Bluetooth wireless adapters, G.ii cards are keyed for A and E slots in a motherboard. Almost M.ii wireless cards support both A and E central slots.
Yard.ii SSD pros and cons
Benefits of using an Yard.2 SSD include:
- Size and capacity. In a laptop, an M.2 SSD takes up far less space and uses much less power than a standard SATA or Series-Attached SCSI (SAS) interface solid-land bulldoze. Yet, if massive storage capacity is required in a mobile device, other class factors will likely be a better fit.
- Performance. An 1000.ii SSD based on the NVMe specifications, for example, can read and write at much faster rates than SATA or SAS SSDs.
- Flexible interface. An M.ii SSD supports PCIe, SATA, USB 3.0, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. If a user purchases a laptop with an Chiliad.2 interface, they will have many configuration options for peripheral gear.
Nevertheless, some of the drawbacks that come with M.ii SSDs include:
- Price. An M.ii SSD costs more than a SATA SSD. Prices for 2.5-inch SATA SSDs have plummeted, as they are produced in greater numbers.
- Limited capacity. While 1 TB or ii TB is probably adequate for most mobile applications, enterprise storage systems crave higher capacities.
What are the buying options for Thousand.ii SSD?
Chiliad.2 cards are typically used in newer mobile computing devices. Because the form factor is unlike from mSATA cards, M.2 SSDs are not compatible with older systems and may not fit large enterprise storage devices. However, enterprise storage vendors are beginning to incorporate Chiliad.2 SSDs in their hybrid and all-flash storage arrays. Even with limited capacities, the size and density of One thousand.ii SSDs still enable storage vendors to pack a lot of high-performance capacity into a small area.
Some examples of different G.2 SSDs to cull from include the Adata XPG SX8200 Pro or Samsung 970 EVO Plus. Storage operation specifications for the Adata M.2 SSD include 256 gigabyte (GB) to 2 TB storage capacity, with read and sequential write speeds up to 3,500 MB and 3,000 MB per 2d, respectively. Its mean time between failures (MTBF) is rated at ii million hours. Random access speeds fall short compared to other choices, withal -- meaning the storage speed may be slower, insufficiently.
G.2 vendors
The price for a 2 TB M.2 SSD typically ranges from $150 to $200; lower capacities are considerably less expensive, with 256 GB M.2 SSDs available for around $l. As noted above, Adata and Samsung, for example, sell a variety of Thousand.two SSDs in unlike capacities. Other M.2 SSD vendors include:
- Crucial, which is owned by Micron Technology
- Kingston Engineering science
- Plextor
- Squad Group
- Toshiba
In addition, Intel is the largest vendor of One thousand.2 wireless adapters.
How do you lot choose an Grand.2 SSD?
Thousand.2 SATA drives and 1000.2 NVMe drives are becoming the standard recommendation for new PC builds and upgrades, as they are becoming less expensive and more than popular.
The first consideration when planning to purchase an M.2 device for a computer is whether information technology has 1 or two Thou.2 plugs. If a laptop is compatible with M.2 specifications, it will accept the concrete interface, and the device'due south operating system should already include the required Advanced Host Controller Interface drivers need to enable installation of the One thousand.2 storage carte. Information technology may besides be necessary to make an adjustment in the device'southward basic input/output organization and then that information technology can recognize the Thousand.2 storage.
If the estimator volition be used mainly for daily tasks or gaming, so an M.2 SATA bulldoze should suffice. Notwithstanding, if the user needs the best calculating speed or requires fast sequential read and write speeds for apply cases such every bit editing 4K video or large file transfers, then an G.2 NVMe drive should be selected.
If the motherboard does non accept an M.2 slot, then the user tin get a Thou.2 bulldoze on a card, which vendors like Asus or MSI provide. These put the K.2 bulldoze on a PCIe expansion card, enabling the use of an M.ii through the PCIe slots.
What are the differences between Grand.2, mSATA and NVMe SSDs?
Thou.ii is normally referred to every bit an mSATA replacement, just mSATA SSDs still exist and may continue to for some time -- especially, in laptop platforms that support that grade factor. Because M.2 and mSATA cards are different and take different connectors, they cannot be plugged into the same devices -- pregnant they both yet have their use cases.
1000.two is a form gene that tin have the form of a SATA SSD or a PCIe NVMe SSD.

M.2 SSDs are faster and store more data than most mSATA cards. 1000.2 SSDs support a variety of interface standards such as PCIe 3.0, SATA iii.0 and USB 3.0 interfaces, compared to mSATA, which just supports SATA interface standards. M.two SATA SSDs take a like level of performance to mSATA cards, but One thousand.2 PCIe cards are notably faster. In addition, SATA SSDs have a maximum speed of 600 MB per 2nd, while Thou.ii PCIe cards tin hit four GB per 2d.
PCIe support besides allows Yard.ii cards to take advantage of the NVMe protocol. An NVMe drive provides a large performance advantage over drives based on other types of interfaces due to reduced latency, increased input/output operations per second and lower power consumption.
The principal benefit of an NVMe-based PCIe SSD over SATA and mSATA is speed. While SATA drives clock in at 750 MB per second, NVMe clocks in at 1 GB per 2nd on the low cease.
Given the speed benefits of the NVMe drives, M.2 NVMe SSDs are a good choice for hard bulldoze-intensive workloads or workloads that require many hard drive reads and writes.
Larn how NVMe stacks up confronting serial-attached SCSI. Specifically, how they compare when it comes to flexibility, performance, scalability and manageability.
Come Configurare Un Ssd M2,
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchstorage/definition/M2-SSD
Posted by: lucktope2001.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Come Configurare Un Ssd M2"
Post a Comment